St Paul, MN – MD Biosciences announces that it has entered into a research agreement with one of the Top 10 pharma companies for screening a library of compounds. MD Biosciences will apply its innovative screening platform, Senerga®, to the pharma company’s compound library with the primary objective of increasing the chances of discovery efficacy on a broader and more efficient basis. These compounds can then be selected based on pharmaceutically relevant activity to be further developed by the sponsor.
“Exploring novel, high-value applications for compounds based on our Senerga® Platform is the core strength of MD Biosciences. We are very excited about this compay engaging MD Biosciences in this important program. It is a great company, sharing our vision in evolving new and efficient ways in the discovery process” said Eddie Moradian, CEO of MD Biosciences.
About the Senerga® Screening Platform
MD Biosciences has a long history of working on complex programs for mechnism of action screening, and efficacy. By conceptualizing a platform that provides algorithmic analysis of a combination of efficacy, biomarker, mechanistic and safety/behavior data, clients are able to broadly screen compounds on the basis of effects on cells, tissues and whole organisms in disease modification without the necessity of prior knowledge of therapeutic pathways. Senerga® screening is a customized approach through in vitro and in vivo models selected to give the broadest screen based on the compound library.
About MD Biosciences
MD Biosciences is a global preclinical research group and contract research organization (CRO) working with biopharmaceutical and medical device companies in an effort towards progressing discovery and development programs to clinical stages. MD Biosciences provides a broad range of services focused in inflammatory, neurodegenerative/CNS, pain, dermal, metabolic and cardiovascular conditions with a particular emphasis on the interplay between the immune, nervous and cardiovascular systems and the conditions that arise in the cross talk between them. Utilizing innovative approaches to efficacy and screening models, MD Biosciences has played a key role for our clients in multi-year programs that have involved respositioning/developing compounds, out-licensing compounds and screening compound libraries. MD Biosciences diverse portfolio of clients includes some of the world’s largest and most well-known pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
--------------------
The information in this press release should be considered accurate only as of the date of the release. MDB has no intention of updating and specifically disclaims any duty to update the information in these press releases.

 MD Biosciences releases a new line of in vivo
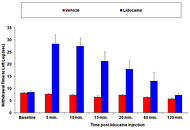
MD Biosciences releases a new line of in vivo  MD Biosciences article Characterization of a porcine model of post-operative pain (POP)
MD Biosciences article Characterization of a porcine model of post-operative pain (POP)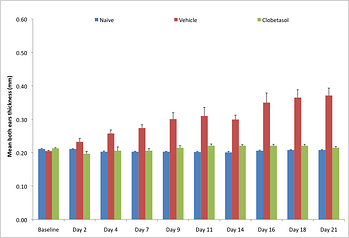 The IL-23 psoriasis model is 21 days long and involves the injection of IL-23 into the ear of C57Bl/6, which produces psoriasis-like inflammation that is dependent on IL-22. IL-22 induces keratinocyte proliferation and epidermal hyperplasia contributing to epidermal thickening. “We are continually looking to the most recent research clinical findings. With the number of clinical trials involving targets in the IL-23/Th17 pathway, offering rapid preclinical models of psoriasis involving this pathway allows biopharma companies to cost-effectively screen potentially novel therapeutics. This is important for companies in early discovery to be able to evaluate compounds in a clinically relevant model of psoriasisform inflammation.”
The IL-23 psoriasis model is 21 days long and involves the injection of IL-23 into the ear of C57Bl/6, which produces psoriasis-like inflammation that is dependent on IL-22. IL-22 induces keratinocyte proliferation and epidermal hyperplasia contributing to epidermal thickening. “We are continually looking to the most recent research clinical findings. With the number of clinical trials involving targets in the IL-23/Th17 pathway, offering rapid preclinical models of psoriasis involving this pathway allows biopharma companies to cost-effectively screen potentially novel therapeutics. This is important for companies in early discovery to be able to evaluate compounds in a clinically relevant model of psoriasisform inflammation.”